Lidarmos: Revolutionizing Machine Perception and Intelligent Automation
Introduction
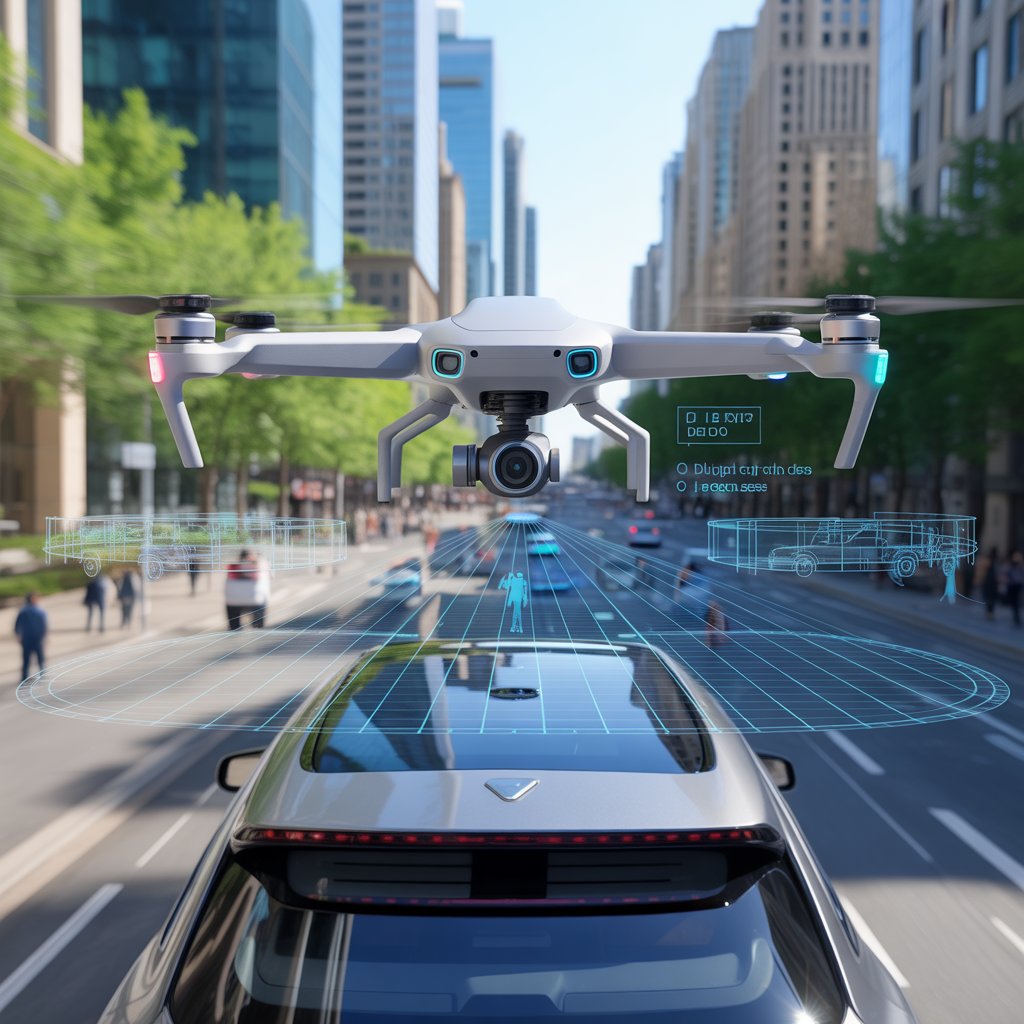
In an era where precision, automation, and data-driven decision-making define progress, Lidarmos emerges as a transformative force in sensing and perception technologies. By integrating LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) with artificial intelligence, robotics, and autonomous systems, Lidarmos creates a cohesive ecosystem for high-accuracy 3D mapping, object detection, and environmental understanding. This technology goes beyond traditional sensing methods by combining laser-based distance measurement with intelligent data processing, enabling machines to perceive and interact with their surroundings in real-time.
Thank you for reading this post, don’t forget to subscribe!In today’s world, where autonomous operations are increasingly common—from self-driving cars navigating complex urban streets to drones monitoring expansive agricultural fields—reliable perception is the foundation of safety, efficiency, and innovation. Lidarmos innovation addresses critical gaps in conventional systems, such as managing dynamic objects, processing large datasets rapidly, and operating under challenging conditions. Across sectors, Lidarmos offers notable advantages, including enhanced accuracy, cost efficiency, and scalable deployment. This article explores the core of Lidarmos, covering its features, applications, benefits, and future potential.
Overview of Lidarmos
At its core, Lidarmos builds on LiDAR principles, using pulsed laser light to measure distances with exceptional precision. Rapid laser pulses reflect from surfaces to generate dense point clouds—detailed 3D representations of environments. What sets Lidarmos apart is its seamless fusion with AI algorithms and robotic frameworks, turning raw data into actionable insights.
The workflow is sophisticated: laser emitters send pulses, receivers capture reflections, and integrated processors—often powered by deep learning—analyze the data for object classification, motion detection, and semantic segmentation. This allows Lidarmos solutions to distinguish between static and moving elements, filter noise, and build persistent maps in dynamic settings.
Historically, LiDAR systems were bulky, expensive, and limited to static mapping. Today, Lidarmos technology has miniaturized hardware, improved resolution, and incorporated AI for real-time processing, making it suitable for mobile and embedded applications. For example, a drone equipped with Lidarmos surveying a construction site can create a high-fidelity 3D model while identifying moving machinery, alerting operators to potential hazards instantly.
Key Features and Capabilities

Lidarmos offers a robust set of capabilities that elevate it beyond traditional LiDAR systems:
High-resolution 3D mapping: Sub-centimeter accuracy using advanced laser scanners and multi-return pulse detection.
Real-time moving object segmentation (MOS): Neural networks distinguish dynamic objects like vehicles or pedestrians from static backgrounds for predictive modeling and collision avoidance.
AI integration: Deep learning models perform semantic segmentation, labeling roads, buildings, foliage, and more. Edge computing ensures low-latency decision-making.
Multi-spectral and long-range sensing: Different wavelengths improve performance in adverse conditions like fog or rain.
Compact hardware: Lightweight, portable units for drones or handheld applications.
Data fusion: Integrates with cameras, radar, or GPS to enhance perception accuracy.
Through techniques like point cloud clustering and temporal filtering, Lidarmos delivers actionable insights, driving operational excellence and ethical AI practices.
Applications Across Industries
Autonomous Vehicles & Transportation: Self-driving cars use Lidarmos for real-time 3D maps, lane detection, and traffic tracking. Urban prototypes show error reduction of over 90% compared to camera-only systems.
Architecture & Construction: High-accuracy site surveys generate as-built models, enabling early clash detection in BIM workflows. Large infrastructure projects have saved millions in rework costs using Lidarmos scanning.
Environmental Monitoring & Agriculture: Drone-based Lidarmos systems map terrain, monitor rivers, and assess crop health. Canopy penetration enables precise vegetation analysis for sustainable practices.
Robotics & Manufacturing: Warehouse robots avoid obstacles and scan inventory, while industrial arms perform precise object detection in cluttered settings.
Other Applications: Archaeology, smart city planning, and disaster response all benefit from rapid mapping, enhanced situational awareness, and actionable data insights.
Benefits and Advantages

Lidarmos offers several key benefits:
Unparalleled precision: Sub-centimeter resolution outperforms traditional surveying methods.
Speed & efficiency: Millions of points per second processed with AI reduces project timelines drastically.
Safety in hazardous areas: Drones and vehicles can access areas unsafe for humans.
Cost savings: Lower operational expenses and scalable deployment ensure economic viability.
Data-driven decision-making: Reliable data supports environmental management, resource allocation, and improved outcomes.
Compared to alternatives like photogrammetry, Lidarmos performs reliably in low-light or featureless environments. Controlled tests show error rates often below 1%, ensuring high reliability.
Current Trends and Innovations
Lidarmos continues evolving rapidly:
Miniaturization: Solid-state systems replace mechanical scanners, improving durability and efficiency.
AI & machine learning integration: Predictive mapping, anomaly detection, and autonomous perception capabilities are accelerating.
Cost reduction: Mass production and innovative materials (e.g., VCSEL lasers) make technology accessible for broader applications.
Sustainability: Energy-efficient designs and climate monitoring applications.
Advanced sensing: Flash LiDAR for instantaneous captures and FMCW technology for measuring velocity alongside distance.
Research also emphasizes ethical AI, bias mitigation, and inclusive technology deployment, ensuring broader adoption.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, Lidarmos faces some challenges:
High initial costs: Premium systems may be expensive, though affordability is improving.
Data volume: Large point clouds require substantial storage and processing power.
Performance in adverse conditions: Heavy rain, dust, or fog can affect accuracy.
Regulatory concerns: Privacy and safety standards must be addressed.
Technical limitations: Range-resolution trade-offs and potential AI biases.
Ongoing innovations, such as hybrid systems and improved noise filtering, aim to address these hurdles.
Future Outlook and Potential

The future of Lidarmos is promising:
Quantum sensing and nanotechnology could enhance resolution and range.
Integration with 6G networks and edge AI will enable swarm robotics and interconnected smart systems.
Autonomous mobility: Lidarmos will support Level 5 autonomy.
Environmental science applications could revolutionize global monitoring efforts.
Consumer applications: AR devices and home robotics are emerging.
The economic and industrial impact of Lidarmos is expected to be significant, creating efficiency gains and new markets while enabling smarter, safer, and more automated systems.
Conclusion
Lidarmos stands at the forefront of machine perception, blending precision sensing with AI-driven intelligence to redefine interaction with physical spaces. Its key features, versatile applications, and numerous advantages position it as a transformative technology across industries. Current innovations and future potential highlight Lidarmos’s role in creating smarter cities, safer transportation, and better environmental understanding. Embracing Lidarmos today prepares industries and societies for an intelligent, automated tomorrow.