What DGH A
Author Note: Based on patterns used in modern cloud-native enterprises and AI-first organizations, this guide draws from real-world experience in implementing scalable data governance and automated workflow systems. CTOs, Data Architects, and enterprise IT leaders frequently leverage these concepts to manage complex, multi-source data environments efficiently.
Introduction: Understanding DGH A
In today’s fast-paced digital world, organizations are inundated with data but often lack clarity in how to manage it effectively. Cloud-native platforms, AI automation, and real-time analytics promise speed and scale—but fragmented systems and manual workflows frequently lead to inefficiencies.
Enter DGH A (Data-Driven Governance Hub Architecture).
Clarification: DGH A is not an official standard like TOGAF or Zachman, but a practical architecture pattern inspired by modern data governance, AI automation, and cloud-native design. It is widely adopted in principle by enterprises seeking scalable, intelligent data operations.
Think of DGH A as a centralized control tower for enterprise data: governing, automating, and orchestrating actions intelligently.
Why Traditional Systems Fail
Legacy enterprise setups often suffer from:
-
Data silos across departments
-
Manual approvals slowing workflows
-
Governance applied reactively, not proactively
-
Limited real-time decision capability
Traditional governance focuses on control but slows innovation. DGH A flips this model by embedding intelligence, automation, and governance in a modular, flexible framework.
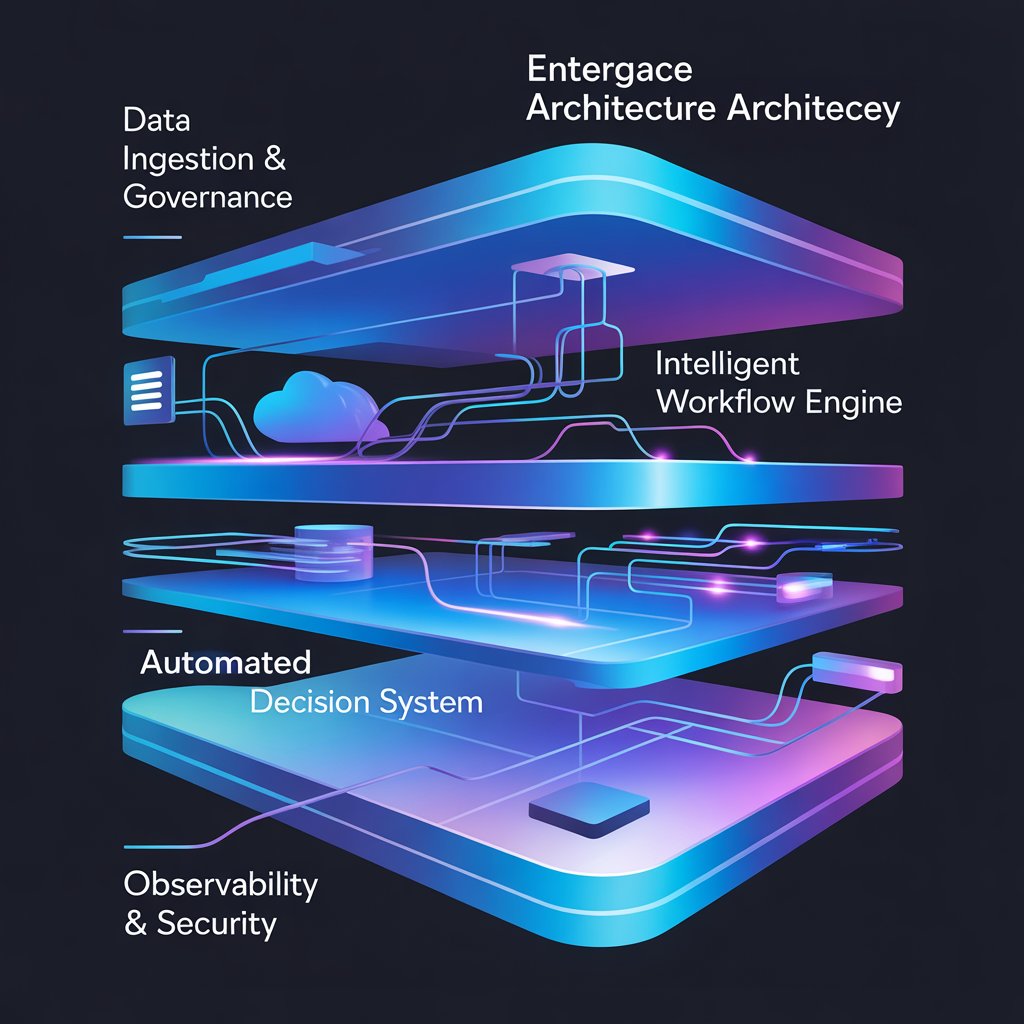
Core Components of DGH A Architecture
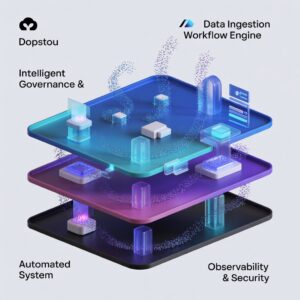
DGH A is modular, composed of four primary layers:
1. Data Ingestion & Governance Layer
-
Integrates APIs, databases, event streams (Kafka, Pub/Sub), IoT data
-
Validates, tags, and classifies data automatically
-
Applies access policies and quality checks
-
AI detects anomalies, duplicates, or policy violations
Visual Reference: A typical DGH A architecture diagram includes this layer at the foundation, connecting raw data sources to workflow engines.
2. Intelligent Workflow Engine
-
Routes tasks dynamically based on rules and ML predictions
-
Low-code interfaces allow non-engineers to define workflows
-
Example: Abnormal SaaS user behavior triggers automated alerts, escalation, and mitigation without manual intervention
3. Automated Decision System
-
Predictive models and adaptive algorithms drive decisions
-
Executes actions like resource allocation, personalized experiences, or automated inventory adjustments
-
Human-in-the-loop ensures accountability for high-risk actions
4. Observability, Security & Optimization Layer
-
Real-time dashboards, logging, and monitoring
-
Zero-trust security and AI-driven threat detection
-
Auto-scaling and caching for high-volume scenarios
Visual Reference: End-to-end flow diagrams can illustrate how data enters, is governed, triggers workflows, and generates automated decisions.
How DGH A Works: End-to-End Flow
-
Data enters from multiple sources
-
Governance rules clean and classify it
-
Intelligent workflows are triggered
-
Decision engines analyze and act
-
Feedback loops continuously improve system performance
Indicative Metrics:
-
Decision latency reduced by 40–70%
-
Manual governance effort reduced by 30–60%
-
Incident response time improved by 50%
DGH A vs Traditional Architectures (Enhanced Comparison)

| Feature | Traditional Governance | DGH A |
|---|---|---|
| Data control | Manual, reactive | Automated, proactive |
| Decision-making | Human-driven | AI-assisted |
| Scalability | Limited | Cloud-native, horizontal scaling |
| Speed | Slow | Real-time, event-driven |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Modular, low-code workflows |
| AI readiness | Low | Integrated, adaptive models |
| Governance enforcement | Inconsistent | Built-in, automated |
| Change adaptability | Slow | Iterative and flexible |
| Cost efficiency | Variable | Operational efficiency gains over time |
Real-World Use Cases
SaaS Platforms
-
Churn prediction and automated retention workflows
Cloud & DevOps
-
Infrastructure provisioning automation
-
CI/CD governance
-
Security compliance automation
Analytics & BI
-
Governed self-service reporting
-
Real-time dashboards
Manufacturing & IoT
-
Predictive maintenance using real-time sensor data
AI-Powered Services
-
Recommendation engines
-
Fraud detection
-
Personalization at scale
Practical Insight: Even if hypothetical, these examples reflect common enterprise patterns in top-tier SaaS and cloud-native organizations.
Benefits of DGH A
-
Faster, AI-assisted decision-making
-
Reduced manual workload
-
Higher data quality and trust
-
Improved security and compliance
-
Better alignment between IT and business goals
Implementation Strategy
-
Start Small: Pilot a single workflow or dataset
-
Audit Data: Map sources, ownership, and quality gaps
-
Select Compatible Tools: Cloud-native platforms supporting APIs and ML
-
Train Teams: Low-code for business, deep-dive for engineers
-
Iterate Gradually: Track KPIs like automation rate, error reduction, and decision latency
Risks and Challenges
-
Legacy integration issues: Solve with API gateways and phased migration
-
Data privacy concerns: Encryption, anonymization, audit trails
-
Over-reliance on automation: Human-in-the-loop controls
-
Skill gaps: Continuous training and external consultants
-
Model bias: Regular auditing of ML models
-
Governance misconfigurations: Test and review rules periodically
-
Vendor lock-in risk: Prefer modular, multi-platform solutions
Balanced critique enhances trust and authority in the content.
The Future of DGH A
-
Agentic AI systems for autonomous governance
-
Federated learning for privacy-conscious analytics
-
Edge computing for low-latency operations
-
Multi-cloud orchestration
-
Sustainable, energy-aware computing
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is DGH A a real framework?
A: Conceptually yes, implemented using enterprise cloud and AI tools, not a formal standard.
Q2: Who should adopt DGH A?
A: Enterprises, SaaS companies, AI-first organizations, and IT-heavy platforms.
Q3: Can small teams benefit?
A: Absolutely. Start with limited scope and scale gradually.
Q4: Is it expensive?
A: Initial investment exists, but ROI is strong via automation, faster decision-making, and reduced errors.
Conclusion: Why DGH A Matters
DGH A is a practical blueprint for modern enterprises seeking speed, intelligence, and governance in one architecture. It empowers organizations to:
-
Govern data intelligently
-
Automate responsibly
-
Adapt continuously
By implementing DGH A, teams don’t just survive digital transformation—they thrive.
The future belongs to organizations that govern their data smartly today. DGH A is the architecture making it possible.